Your heart works tirelessly, pumping blood and supporting your health. Supplements like omega-3s, CoQ10, cocoa flavanols, and magnesium can help improve circulation, lower triglycerides, regulate blood pressure, and support energy production. By 2025, evidence-backed options are key to making informed choices.
Key Takeaways:
- Cocoa flavanols improve blood flow and reduce inflammation. Products like Naturalis High Flavanol Cocoa deliver 450–500 mg per serving, supporting arterial health.
- Omega-3s (EPA & DHA) lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and stabilize heart rhythms. Aim for 1,000–2,000 mg daily.
- CoQ10 boosts energy production and offsets statin-related depletion. A dose of 100–200 mg daily is common for heart health.
- Magnesium supports blood pressure and heart rhythm. Forms like magnesium citrate or glycinate are more absorbable.
These supplements work best alongside a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, exercise, and stress management. Always consult your doctor before starting any new supplement, especially if you take medications.
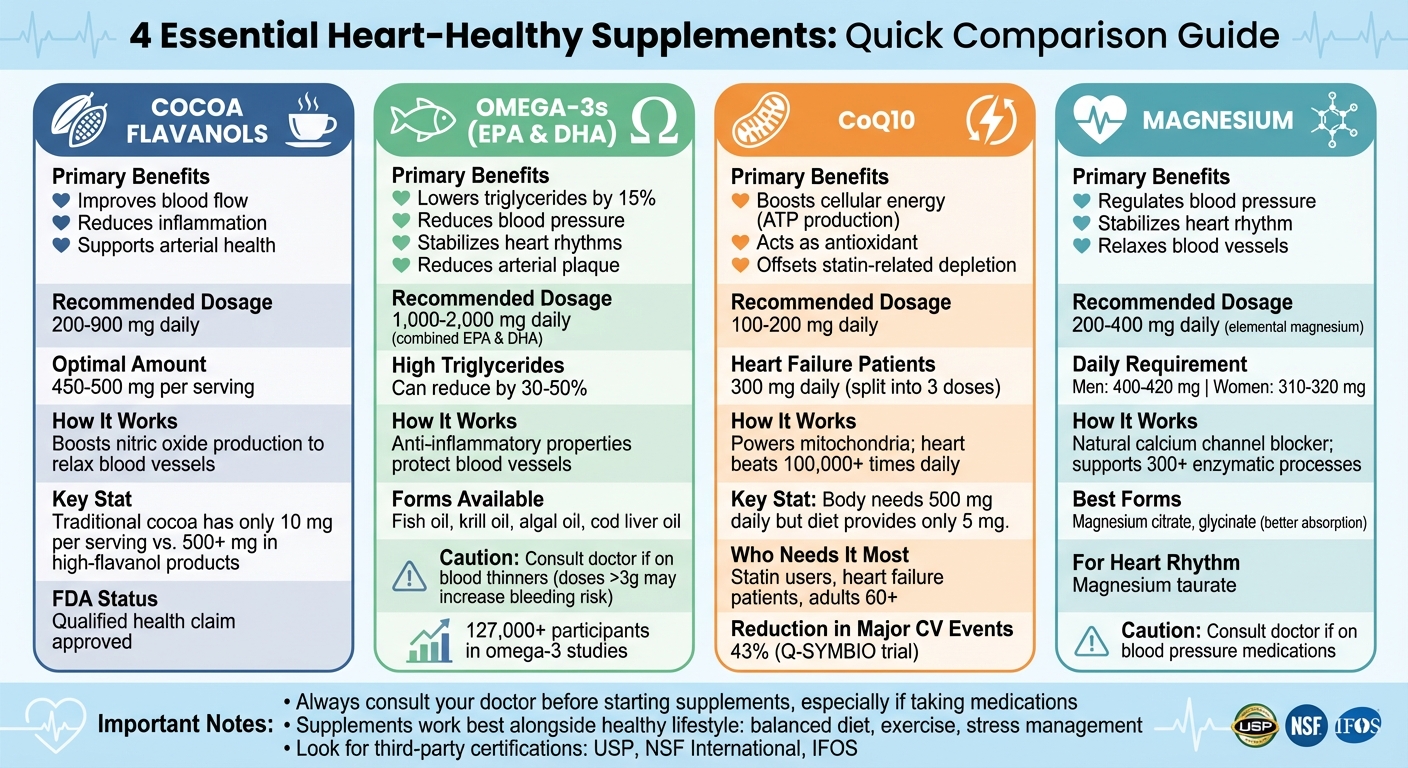
Heart-Healthy Supplements Comparison: Benefits, Dosages, and Key Features
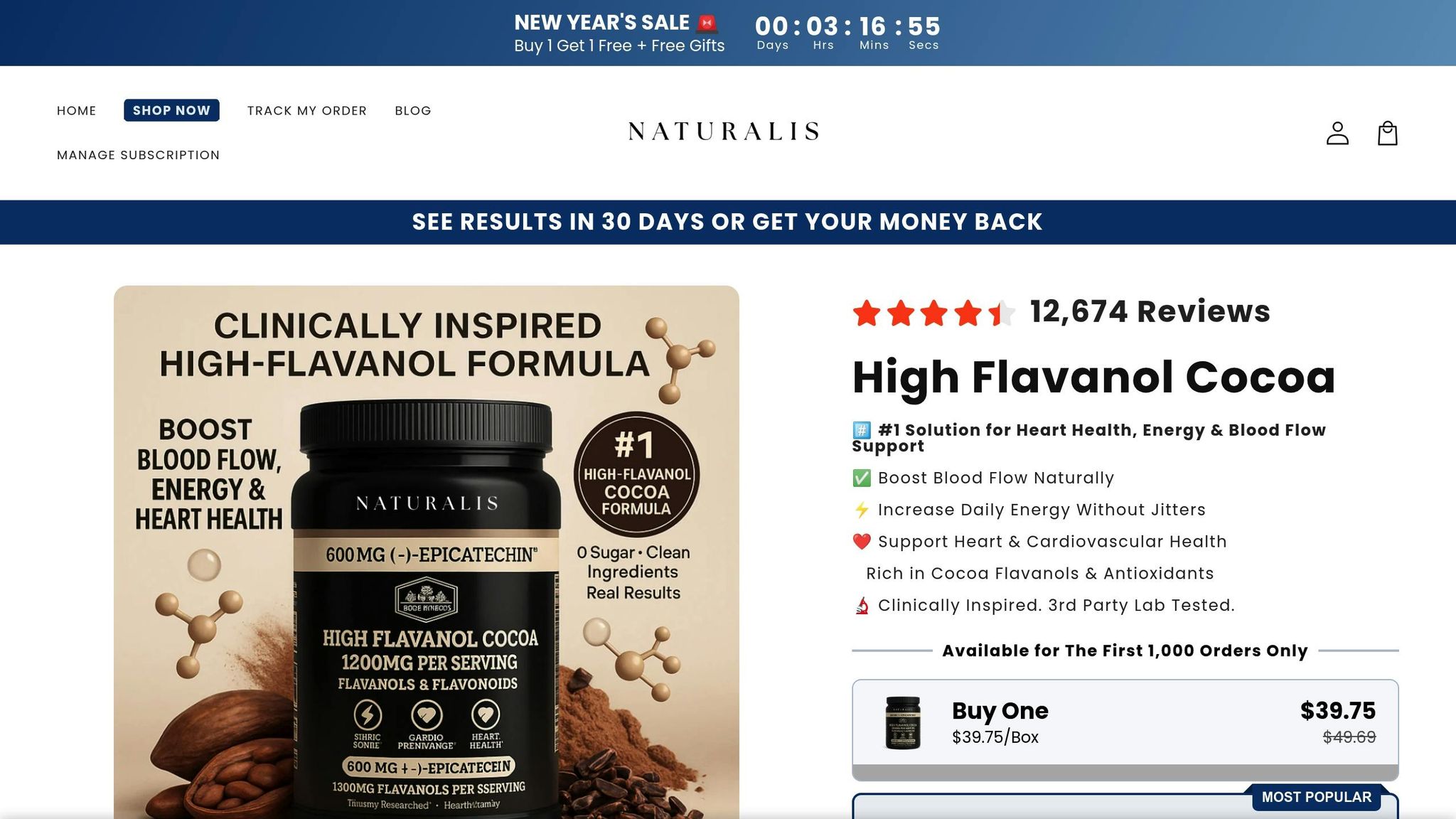
Naturalis High Flavanol Cocoa: Supporting Circulation and Heart Health
How Cocoa Flavanols Support Your Heart
Cocoa flavanols, natural compounds found in cacao beans, play a key role in promoting better blood flow. They do this by boosting nitric oxide production, which helps blood vessels relax and widen. This improved circulation benefits the entire body, from the brain to the extremities.
"Cocoa flavanols... induce vasodilation of the peripheral and cerebral vascular system, increasing brain blood flow and perfusion mainly through an improvement in nitric oxide bioavailability in endothelial cells."
– Daniela Mastroiacovo et al., American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Studies have shown that consuming 993 mg of cocoa flavanols daily over eight weeks led to noticeable improvements in blood pressure and insulin resistance in older adults. These compounds may also help protect LDL cholesterol from oxidation, a critical step in preventing the buildup of arterial plaque.
For heart health, research suggests that a daily intake of 200 mg to 900 mg of cocoa flavanols can lead to modest improvements in cardiovascular function. However, traditional cocoa processing methods, like alkalization, can strip flavanol content down to as little as 10 mg per serving. In contrast, high-flavanol cocoa products retain over 500 mg per serving, making them a much more effective option.
Naturalis High Flavanol Cocoa takes full advantage of these benefits by using advanced techniques to preserve flavanol levels.
What Sets Naturalis Cocoa Apart
Naturalis High Flavanol Cocoa stands out thanks to its innovative processing methods, which keep the beneficial flavanols intact - compounds often lost during standard chocolate production. Each serving packs a concentrated dose of flavanols in a sugar-free formula, offering daily cardiovascular support without the extra calories typically found in dark chocolate.
Clinical studies back up its effectiveness. For example, healthy adults who consumed approximately 400 mg of cocoa flavanols twice a day for a month saw a 21% improvement in blood vessel function. A single serving of high-flavanol cocoa provides 450–500 mg of flavanols - nearly six times the amount found in 80% dark chocolate.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has even approved a qualified health claim for high-flavanol cocoa powder containing at least 4% naturally retained flavanols, suggesting it may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. With a price of $49.69 per container (around $1.66 per day), Naturalis offers an accessible way to support heart health, backed by over 20 years of research and more than 30 clinical studies.
sbb-itb-e973f61
Omega-3 Fish Oil: Heart and Blood Vessel Support
How Omega-3s Help Your Heart
Omega-3 fatty acids are a cornerstone for heart health, with EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) leading the charge. These essential fats, primarily sourced from marine life, offer several benefits: they help lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and combat arterial plaque buildup. Beyond that, their anti-inflammatory properties protect blood vessels and decrease the risk of atherosclerosis.
A 2020 review analyzing 23 studies with nearly 44,000 participants found that EPA and DHA could reduce triglycerides by about 15%. For individuals with very high triglycerides (over 500 mg/dL), prescription-strength omega-3s can slash levels by 30% to 50%. Another meta-analysis of 71 clinical trials revealed that consuming 2 to 3 grams of EPA and DHA daily significantly lowered both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
"Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA found in fish oil... reduce triglycerides, support healthy blood pressure, and offer anti-inflammatory benefits to the heart and blood vessels."
– Dr. Iqbal Malik, London Cardiovascular Clinic
These fatty acids also help stabilize heart rhythms, reduce blood clotting, and improve arterial function. A 2019 review of 13 major studies, encompassing over 127,000 participants, showed that marine omega-3s lowered the risk of heart attacks and coronary heart disease-related deaths. The American Heart Association recommends about 1,000 mg of EPA and DHA daily for those with documented coronary heart disease.
For general heart health, aim for 1,000–2,000 mg of combined EPA and DHA daily, especially if you have high triglycerides. However, if you’re taking blood thinners, consult your doctor first, as doses above 3 grams per day may increase bleeding risks.
Next, let’s explore the various supplement options to help you make an informed choice.
Different Forms of Omega-3 Supplements
Omega-3 supplements come in a variety of forms, each offering unique benefits. The most common option is fish oil, derived from cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and anchovies. It provides EPA and DHA in triglyceride or ethyl ester forms, with the triglyceride form being up to 70% more absorbable. Krill oil, another popular choice, delivers omega-3s as phospholipids, which may enhance absorption, although it typically contains less EPA and DHA per gram than fish oil.
For plant-based alternatives, algal oil is a vegan-friendly option that primarily supplies DHA, with some varieties also containing EPA. Studies show algal oil is just as effective as fish oil in raising DHA levels. Another option is cod liver oil, which not only provides EPA and DHA but also naturally includes vitamins A and D.
| Supplement Type | Primary Omega-3 Form | Key Advantage | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish Oil | EPA & DHA | High concentration; well-studied | Choose enteric-coated to avoid fishy aftertaste |
| Krill Oil | EPA & DHA (phospholipids) | May improve absorption | Lower EPA/DHA content per gram |
| Algal Oil | DHA (some EPA) | Vegan-friendly; sustainable | Often more expensive |
| Liquid Fish Oil | EPA & DHA | High concentration | Requires refrigeration |
When choosing a supplement, focus on the specific EPA and DHA content listed on the label rather than the total "fish oil" amount. Opt for products certified by third-party organizations like IFOS (International Fish Oil Standards), USP, or NSF International to ensure quality and purity. If you’re prone to "fishy burps", look for enteric-coated softgels that dissolve in the small intestine instead of the stomach.
Options range from budget-friendly picks like Kirkland Signature Natural Fish Oil, priced at around $21 for 400 capsules, to premium brands like Nordic Naturals Ultimate Omega Liquid, which costs about $38 per bottle. For a mid-range choice, Life Extension Super Omega-3, priced at $23, boasts a five-star IFOS certification for purity and sustainability.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): Energy Production and Heart Function
How CoQ10 Works in Your Body
CoQ10, much like cocoa flavanols and omega-3s, plays a vital role in supporting cellular energy and maintaining heart health. This molecule resides in your mitochondria, where it helps produce ATP - the fuel your cells need to function. Think about this: your heart beats over 100,000 times a day, pumping nearly 5,000 gallons of blood through an intricate network of 60,000 miles of blood vessels. To keep up with this nonstop effort, the heart relies heavily on CoQ10 for the energy it demands.
But CoQ10 isn’t just about energy. It also acts as a powerful antioxidant, shielding cells from oxidative stress and enhancing the effects of other antioxidants like Vitamin E.
"CoQ10 has an important role in helping your cells produce energy. It may also act as an antioxidant."
– Dell Stanford, Senior Dietitian, British Heart Foundation
Here’s the catch: as we age, our natural production of CoQ10 dwindles. While your body needs roughly 500 mg of CoQ10 daily, the average diet only supplies about 5 mg. This shortfall becomes more pronounced under stress or when medications like statins disrupt CoQ10 synthesis.
If you’re considering supplementation, CoQ10 comes in two forms: ubiquinone (oxidized) and ubiquinol (active). Though ubiquinol is often marketed as easier to absorb, ubiquinone is widely researched and efficiently converted by the body. For best results, pair CoQ10 with healthy fats to enhance absorption.
Who Benefits Most from CoQ10
CoQ10’s role in energy production and antioxidant defense makes it especially important for certain groups of people.
Statin users are among the top candidates for CoQ10 supplementation. Statins, while effective at lowering cholesterol, also block the pathway that produces CoQ10, potentially cutting levels by up to 50%. Many cardiologists recommend CoQ10 to help manage statin-related side effects.
"If my patient complains about statin side effects, I always recommend CoQ10. I start with 100 mg of CoQ10. If the statin begins to work, I go up to 150 mg, possibly even 200 mg."
– Dr. John S. Ho, Cardiologist, Cooper Clinic
Although clinical studies provide mixed results on whether CoQ10 reduces statin-related muscle pain, roughly 30% to 40% of patients report feeling better after starting supplementation.
Heart failure patients often have depleted CoQ10 levels, both in their blood and heart tissue. The Q-SYMBIO trial, a 2014 study involving 420 heart failure patients, found that taking 300 mg of CoQ10 daily (split into three doses) alongside standard medications led to a 43% reduction in major cardiovascular events and fewer hospitalizations compared to a placebo group.
Older adults also face declining CoQ10 levels as they age. Production peaks in your 20s and gradually decreases, leaving people over 60 with significantly lower levels. This decline can impact energy production and overall heart function.
For general heart health or to address statin-related depletion, a daily dose of 100–200 mg is commonly recommended. However, always consult your cardiologist before starting CoQ10, especially if you’re on blood thinners like warfarin or certain blood pressure medications.
If you’re exploring supplement options, consider products like California Gold Nutrition CoQ10, priced at about $15.07 for 120 capsules (100 mg each), or Life Extension Super Ubiquinol CoQ10, available for around $42.75 for 60 softgels (100 mg each).
More Supplements That Support Heart Health
Magnesium for Blood Pressure and Heart Rhythm
Magnesium plays a crucial role in over 300 enzymatic processes in the body, including those that support heart health. Acting as a natural calcium channel blocker, it helps relax blood vessels and stabilize heart rhythms. This mineral is essential for regulating the electrical impulses that control your heartbeat, reducing the chances of palpitations and arrhythmias. Additionally, magnesium helps balance sodium and potassium levels, which promotes nitric oxide production - a molecule that widens blood vessels to enhance blood flow and oxygen delivery.
For adults, the daily magnesium requirement is 400–420 mg for men and 310–320 mg for women. Clinical dosages for heart health often range between 200–400 mg of elemental magnesium per day. Among the various forms, magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are favored for their superior absorption and gentle impact on digestion. If your focus is specifically on heart rhythm, magnesium taurate is worth considering. This form combines magnesium with taurine, an amino acid known for its cardiovascular benefits.
However, if you're on blood pressure medications, consult your doctor before adding magnesium to your routine. Magnesium can amplify the effects of these medications, potentially lowering blood pressure too much. Those with kidney disease should also approach supplementation cautiously, as impaired kidney function can affect magnesium regulation.
Next, let’s explore how fiber supplements can help manage cholesterol levels.
Fiber Supplements for Cholesterol Control
Soluble fiber offers a unique approach to heart health by binding cholesterol in the digestive tract, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
"Psyllium is a source of soluble fiber, meaning it can bind to cholesterol and help remove it from the body before it's absorbed."
– Adiana Castro, M.S., RDN, Owner of Compass Nutrition
For overall health, experts recommend a daily fiber intake of 25 to 30 grams, with men under 51 aiming for 38 grams. Blond psyllium husk, in particular, has been shown to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol while boosting HDL (good) cholesterol. Start with 3 grams per day and gradually increase to 10 grams as your body adjusts.
To maximize the benefits of fiber supplements, make sure to drink plenty of water to keep the fiber moving smoothly through your digestive system. Take these supplements separately from medications, and increase your dosage gradually to minimize any digestive discomfort.
Moving on, vitamin D also plays a key role in maintaining heart health.
Vitamin D and Heart Disease Risk
Vitamin D receptors are found throughout the cardiovascular system, influencing everything from inflammation control to vascular function. Alarmingly, about 30% of adults in the U.S. have insufficient levels of vitamin D. Low levels have been associated with increased risks of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, and stroke.
While maintaining adequate vitamin D levels is important, taking excessive amounts is not beneficial. The Vitamin D and Omega-3 Trial (VITAL), which included 25,874 participants, found that supplementing with 2,000 IU of vitamin D daily did not significantly lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death compared to a placebo.
"It takes only small-to-moderate amounts of vitamin D to have optimal cardiovascular function. More is not better."
– JoAnn E. Manson, M.D., Dr.P.H., Chief of the Division of Preventive Medicine at Brigham and Women's Hospital
Stick to the Recommended Dietary Allowance: 600 IU daily for adults up to age 70, and 800 IU for those 71 and older. Avoid exceeding 4,000 IU per day without medical supervision, as high doses can lead to elevated calcium levels and arterial deposits. If you're unsure about your vitamin D levels, consider a 25(OH)D blood test, especially if you have risk factors like obesity, darker skin, or absorption issues.
Finally, taurine is another nutrient that quietly supports heart health.
Taurine: A Lesser-Known Heart Nutrient
Taurine, a naturally occurring amino acid, works synergistically with magnesium (as in magnesium taurate) to stabilize heart rhythms and maintain the heart's electrical balance. Including taurine in your heart health regimen can provide an extra layer of support for cardiovascular function.
Supplements and Heart and Vascular Health
How to Choose Quality Heart Supplements
When it comes to supporting your heart health, picking the right supplement is just as important as selecting the right ingredients. Since supplements don’t undergo pre-market review by the FDA, it’s crucial to rely on third-party certifications like USP, NSF International, or ConsumerLab.com to ensure quality.
"A USP stamp indicates that the supplement has voluntarily been submitted to the USP Dietary Supplement Verification Program for testing and auditing. This indicates the product was properly manufactured, contains the ingredients listed on the label and does not contain harmful levels of contaminants."
– Justin Arunthamakun, MD, FACC, Cardiologist
Pay attention to clearly labeled dosages and the bioavailability of ingredients. Look for transparency in labeling, with exact amounts listed (e.g., 500 mg EPA, 250 mg DHA). Opt for forms that are more easily absorbed, like ubiquinol for CoQ10 or magnesium glycinate or citrate for magnesium.
Be cautious of warning signs that could indicate poor quality. For instance, an analysis revealed that 4 out of 11 red yeast rice products contained citrinin, a toxin linked to kidney failure. Similarly, if you’re considering cocoa supplements, steer clear of products labeled as "alkalized" or "Dutch-processed." These processes drastically reduce beneficial flavanols, cutting epicatechin content from 10–15 mg per tablespoon to just 1–3 mg.
Lastly, prioritize supplements supported by human clinical trials rather than relying on animal studies or marketing hype. Check that the label specifies clinically effective dosages - for example, at least 2 grams of plant sterols or 200–400 mg of elemental magnesium.
Combining Supplements with Heart-Healthy Habits
Supplements work best when paired with lifestyle habits that promote heart health. The most effective strategy blends supplements backed by research with foundational practices like eating a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress effectively.
Start with the Mediterranean diet as your cornerstone. Known for reducing inflammation and protecting blood vessels, this diet is a natural ally for heart health. Adding supplements like omega-3s or cocoa flavanols to this eating plan can further enhance its benefits.
"Diet plays a big part in many of the risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, and diabetes. Watching what you eat will go a long way towards keeping your heart healthy." – Cheng-Han Chen, M.D., Cardiologist
Dietary improvements become even more powerful when combined with regular physical activity. Aim for 150 minutes of aerobic exercise weekly - whether it’s brisk walking, swimming, or cycling - and consider nitric oxide–boosting supplements to improve circulation. If resistance training is part of your routine (at least two days a week), adding whey protein (at least 25 grams per serving) could be beneficial. A 2025 analysis of 21 studies found that combining whey protein with exercise reduced triglycerides after 12 weeks of consistent use.
Stress management is another critical piece of the puzzle. Chronic stress harms blood vessels and fuels inflammation. Incorporating practices like mindfulness, deep breathing, or journaling into your daily routine can amplify the effects of supplements such as CoQ10 or turmeric. With over 48% of U.S. adults experiencing some form of cardiovascular disease, addressing stress at its root is essential for better heart health.
It’s important to remember that supplements are not a replacement for healthy habits or medications - they’re meant to fill in nutritional gaps. For those on statins, for example, CoQ10 supplementation can help support the active lifestyle needed for long-term heart health.
Conclusion: Taking a Natural Approach to Heart Health
Caring for your heart starts with making informed, research-supported decisions. The supplements discussed here, like omega-3s, CoQ10, and magnesium, each bring unique benefits to various aspects of heart health. However, cocoa flavanols stand out due to the robust clinical evidence supporting their role in maintaining arterial flexibility through nitric oxide production.
One standout product, Naturalis High Flavanol Cocoa, provides 450–500 mg of cocoa flavanols per serving - far exceeding the amounts found in traditional cocoa products. The reason? Conventional chocolate processing destroys up to 60% of these delicate compounds, making supplementation a smarter choice. In the COSMOS trial, which included over 21,000 participants aged 60 and older, daily cocoa extract supplementation resulted in an 8.4% annual reduction in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), a key marker of inflammation tied to cardiovascular disease risk.
"While cocoa extract is not a replacement for a healthy lifestyle, these results are encouraging and highlight its potential role in modulating inflammation as we age." – Yanbin Dong, Director, Georgia Prevention Institute
This evidence underscores the value of cocoa flavanols as part of a broader strategy for heart health. With the average person experiencing over 3 billion heartbeats by the age of 75, choosing supplements that deliver bioavailable nutrients - like those rich in (-)-epicatechin - can make a meaningful difference. At $49.69 for a month's supply, Naturalis High Flavanol Cocoa offers a practical, science-supported way to maintain cardiovascular health and energy levels.
Of course, supplements work best when paired with a Mediterranean-style diet, regular physical activity, quality sleep, and stress management. By combining these elements, you’re not just addressing symptoms but creating a well-rounded, long-term plan for heart health. Incorporate these supplements into your daily life to take a proactive, natural approach to supporting your heart for years to come.
FAQs
What are the heart health benefits of cocoa flavanols?
Cocoa flavanols are natural compounds found in cocoa that play a key role in supporting heart health. These compounds enhance blood flow by boosting the production of nitric oxide, which helps relax and widen blood vessels. As a result, they can contribute to maintaining healthy blood pressure and improving overall circulation.
Beyond improving blood flow, cocoa flavanols are also packed with antioxidants. These antioxidants work to protect blood vessels from damage caused by free radicals, which can lead to oxidative stress. By reducing arterial stiffness, they help maintain healthy cardiovascular function. Studies have also shown that consuming cocoa rich in flavanols may improve metabolic markers tied to heart disease, adding another layer of protection against cardiovascular issues.
With these combined benefits, cocoa flavanols can be a meaningful part of a lifestyle focused on heart health.
What is the ideal daily dose of omega-3s for supporting heart health?
Research indicates that taking around 3 grams of EPA and DHA omega-3 fatty acids each day can promote heart health. This amount has been linked to better cardiovascular function and may even help reduce blood pressure levels.
It’s important to talk to your healthcare provider before adding any new supplements to your routine to make sure they’re right for your specific health situation.
Can CoQ10 help reduce muscle pain caused by statins?
CoQ10 supplements might offer relief from muscle pain and discomfort linked to statin use. Statins are widely used to manage cholesterol levels but can occasionally lead to muscle-related side effects. CoQ10, a naturally occurring compound in the body, may help support muscle health and make it easier to tolerate statin therapy.
Before adding CoQ10 to your routine, talk to your healthcare provider. They can help determine if it’s a good fit for you and recommend the proper dosage based on your individual needs.


